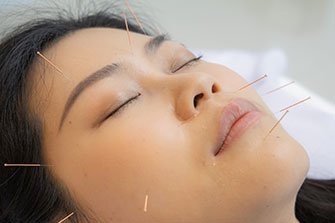
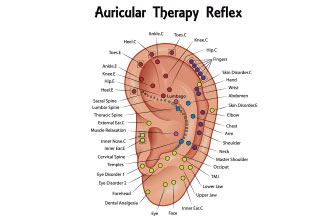
Acupuncture has helped billions of people over the past 5000 years. Acupuncture helps relieve signs and symptoms of many health conditions. In addition, the diagnostic methods of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) uncover the underlying root cause(s) of these conditions. The goal of this ancient health care system is the activate the body’s natural self-healing abilities. It also supports and strengthens the body to prevent future illness and disease
Acupuncture is a safe, natural, effective and drug-free treatment providing the perfect way to get well and stay healthy.